Enabling mod_rewrite in Apache2 on Ubuntu
Permalink Structure
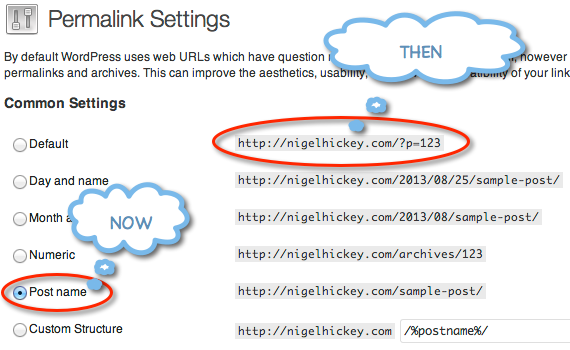
Recently I was looking at my blog URLs and noticed that I was not happy with the current look/structure. I knew that I had to change the Permalink structure from the WordPress defaults to a better looking more easily understandable URL. This would help sharing URL links as well as having that professional feel to them, not to mention some added SEO benefits too.
Well changing your Permalink structure is quite easy in WordPress and can be done in a few steps providing a few things happen 1st on the server side of your blog world. if your blog is hosted somewhere that you do not manage the server config/setup (GoDaddy, Network Solutions, etc) then you can just just right into making the change usually and skip the steps below. If your server is hosted in one of those company’s or somewhere like Amazon’s AWS and you built it/set it up/configure and support it mostly, then you may need to enable “mod_rewrite” on your Linux server.
I found this out the hard way when I jumped right into changing the Permalinks and then got a sweet little 404 error on all of my blog posts and pages…WTF!! That is until a found the quick solution after a few days of digging through the interwebs. Thanks to Dan Nanni of xmodulo.com for his tips on how to enable “mod_rewrite”, be sure to check him out too and learn a bit more about “mod_rewrite”!
To Enable mod_rewrite:
A default installation of Apache2 comes with mod_rewrite installed. Verify the existence of /etc/apache2/mods-available/rewrite.load to prove this point.
1) Enter this – $ cat /etc/apache2/mods-available/rewrite.load
Output – LoadModule rewrite_module /usr/lib/apache2/modules/mod_rewrite.so
2) To enable and load mod_rewrite – $ sudo a2enmod rewrite creates a symbolic link in /etc/apache2/mods-enabled.
3) Next Step – $ ls -al /etc/apache2/mods-enabled/rewrite.load
4) Open up the following file and replace every occurrence of “AllowOverride None” with “AllowOverride all” (I prefer using nano for my edits, you can use your favorite editor)
$ sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/default
5) Restart Apache2 – $ sudo service apache2 restart
Thats it. Done. Next you can jump in to the WordPress Permalinks (found in the URL /wp-admin/options-permalink.php of your blog, or under Settings/Permalinks). Here is a shot of what mine looks like on the Admin side.
Once again I need to thank Dan Nanni of xmodulo.com for posting these steps that I have shared here. Awesome stuff.
Please consider sharing this post with the tools below!